Who we are?
Palintest manufactures a range of advanced water and environmental testing equipment,
and from its Tyneside base exports to over 100 countries across the globe. These products are used in a wide variety of applications to protect the environment and safeguard public health. Crucially Palintest are able to simplify testing for key water quality parameters, enabling critical water quality decisions to be made with confidence.
|
 |
Total Residual Oxidants (TRO)
- Guidelines across the globe
- The problems of transient species
Portable methods:
- DPD method
- Lissamine Green B method
- Other colorimetric methods
- Amperometric Sensor
Laboratory methods:
- Amperometric Titration
- Ion Chromatography
- Spectrophotometric method
- Iodometric titration
Implications on DWI guidelines for TRO?
Total Residual Oxidants
Usually used in the context of chlorine dosing
Can be applied to other oxidants e.g. Chlorine Dioxide and the DBP – chlorate and chlorite
Usually in the context of drinking water
- Chlorite is the primary DBP (50 – 70%)
- Chlorate also produced (dependent on pH conditions)
- Chlorite and Chlorate can be introduced by the generator
- Most generators use chlorite or chlorate precursor chemicals
|
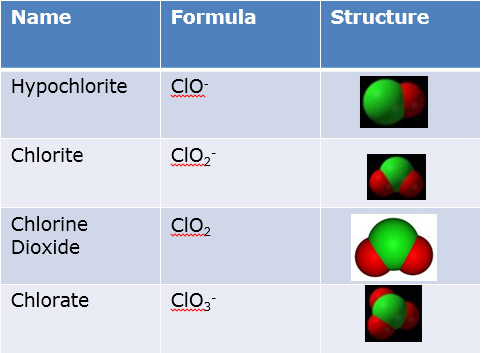 |
1. Total Residual Oxidants mean ClO2, ClO2- and ClO3-
(Within the context of chlorine dioxide dosing)
(May include chlorine if chlorinated water is being treated with ClO2)
DWI Guidelines – Guideline 31
|
BS EN 12671: 2009 – European Standard
Chemicals used for treatment of water intended for human consumption.
|
 |
Chlorine dioxide generated in situ.
Additional national Conditions:
The combined concentration of chlorine dioxide, chlorite and chlorate should not exceed 0.5mg l-1 as chlorine dioxide in the water entering supply.
USEPA – used as a international surrogate standard
|
ClO2 and ClO2- monitored daily
ClO3- monitored monthly
Maximum Disinfectant Residual Levels (defined under DBPR: 2002) 0.8mg/l ClO2 1mg/l ClO2-
|
 |
2. DWI requirements are relatively stringent
ClO2 is highly volatile
- Samples should be taken in amber glassware
- Small headspace
- Minimal agitation
- Testing must be carried out on site and carefully
ClO2- and ClO3- are persistent
- More suitable for sampling and off site analysis
- Off site analysis - issues in real time decision making

3. On site analysis is the best way of complying with DWI
- DPD
- LGB
- Amaranth
- CPR
- ACVK
- ChlordioX™ Plus
|
 |
 |
DPD method
- The ‘Palin system’
- Blue Book method
- US EPA approved method
- Widely accepted method, e.g. EA, HSE
- No longer an AWWA Standard Method (21st edition)
- A general oxidation method, i.e. not selective
- Determination of ClO2 (and ClO2- possible)
- ClO2- method difficult and time consuming
- Can result in negative values if chlorine present
- A ‘difference’ method
- Concerns over chlorite and chloride interference
- Removal as AWWA Standard method
|
   |
4. DPD method is no longer a AWWA standard method for chlorine dioxide
Lissamine Green (LGB)
- US EPA Approved method
- ClO2 specific
- ClO2- determination possible with Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)
|
 |
Dye bleaching method for ClO2
- Time and temperature dependence
- Operator errors
Addition of HRP for ClO2-
- A ‘difference’ method
- Generally non-standard methods for ClO2
- Useful for process optimisation
- Not so good for regulatory reporting
- No ability to quantify ClO2- (or ClO3-)
Amaranth Method
- Popular in Europe
- Small test range
- Generally interferent free
- Dye bleaching method
|
 |
Chlorophenol Red (CPR) Method
- Generally interferent free (ClO2- can be an issue)
Acid Chrome Violet K (ACVK) Method
- Generally interferent free
Dye bleaching method
- Method defined in BS EN 12671:2009
5. Other colorimetric methods are available
6. Colorimetric methods suffers from difficulties in the field
7. Photometric dye bleaching methods can lead to operator error
•Patented Palintest technology for ClO2 and ClO2-
•US EPA Approved method The ONLY portable US EPA approved method for ClO2-
•Enables compliance to US EPA requirements (daily monitoring of ClO2 and ClO2-, monthly for ClO3-)
•Uses standard chemistry (similar to amperometric titration method)
•Not DWI (because of lack of ClO3-)
•Sequential test protocol
•Aims to simplify ClO2 and ClO2- determination
•Can carry out chlorine measurement
•ClO2- is difference method (but not reliant on user) |
 |
8. ChlordioX™ Plus enables compliance with most of DWI requirements
Phương pháp PTN Bao gồm chuẩn độ điện tích Amperometric , Sắc ký ION, Chuẩn độ I ốt, Quang phổ
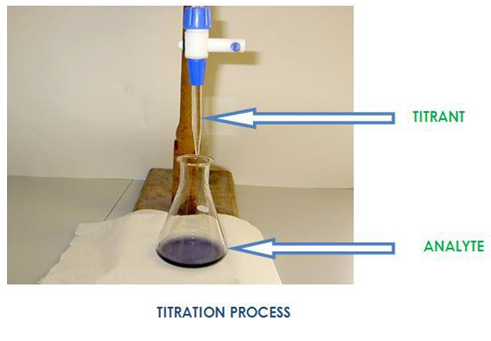
Amperometric Titration
- Sequential titration method
- Titration with PAO or thiosulphate with pH control
- ClO2, chlorine (free and combined), ClO2- and ClO3- possible
- Requires a skilled technician (especially for ClO3-)
|
 |
Ion Chromatography
- The best way to determine ClO2- and ClO3-
- No good for ClO2
- Requires specialist equipment
- Requires careful sample preparation
- Requires skilled technician
|
 |
Spectrophotometry
- UV/Vis (λ = 360nm) spectrophotometry can be used for ClO2
- If ClO2- present, can lead to interferences from intermediate species
- Some manufacturers offer this as a visible region test (λ = ~420nm)
- Interferences more prominent at longer λ
- But portable
- High limit of detection (not suitable for potable water)
- Really only suitable for standard solutions (of high concentration)
|
 |
Iodometric titration
- Same sequential titration principle as amperometric titration
- Suffers from interferences when multiple oxidants are present
- Requires skilled technician
- Really only suitable for standard solutions (and how Palintest standardise solutions)
|
 |
9. Laboratory methods are not conducive to complying with DWI guidelines
10. Is it possible to comply with the DWI guidelines?
- Careful monitoring and dosing control at generator Downstream monitoring must incorporate
- On line monitors
- Sampling for laboratory (IC) assessment
- Portable monitoring
|
 |
10 Things you now know about TRO:
1. Total residual oxidants include ClO2, ClO2- and ClO3- (and chlorine)
2. DWI regulations are relatively stringent
3. On site analysis is the only way of complying with DWI regulations
4. DPD is no longer a standard method
5. Other colorimetric methods are available
6. Colorimetric suffers from difficulties in the field
7. Photometric dye bleaching susceptible to operator error
8. ChlordioX™ Plus enables compliance with most of DWI requirements
9. Laboratory methods alone are not conducive to complying with DWI guidelines
10. It is difficult to comply with the current DWI guidelines

















