CellHesion 300
Liên hệ
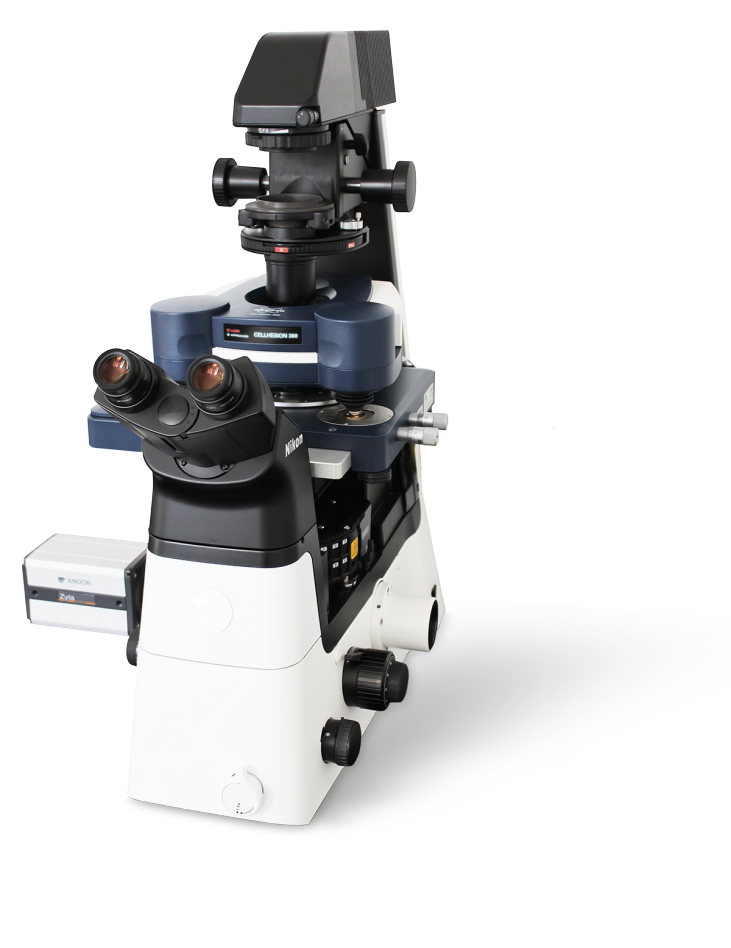
CellHesion® 300
The automated CellHesion® 300 is the ideal tool for measuring cell-cell, cell-tissue, and cell-substrate interactions with single-molecule sensitivity. It enables fast and easy measurement of the structure, morphology, and nanomechanical properties of living biological systems, delivering crucial insights into the role they play in various pathological disorders. This innovative system creates novel possibilities for applications in biophysics, biochemistry, implant research, wound healing, developmental biology, stem cell research, infection biology and immune response studies.
Understanding Biomechanics Made Easy
CellHesion 300 provides reproducible, quantitative data of unprecedented quality. Its high degree of automation increases throughput and delivers the productivity, performance, and statistical significance required for biomedical and clinical research environments. Important parameters, such as maximum adhesion force, individual unbinding events, and tether characteristics are automatically determined from each dataset by innovative software solutions.
Watch our short video and find out how CellHesion 300 can be used to study the relationship between structure and function and the effect of mechanical forces on cells and tissues, opening new possibilities for applications in fields such as developmental biology, tissue engineering, and nanomedicine.

Only CellHesion 300 delivers:
- Maximized throughput for higher productivity by automating measurements
- Correlative and label-free multiparametric, nanomechanical measurements of living samples in near-physiological conditions
- Fast and simple selection of regions of interest over large sample areas, ideal for tissue biopsies
- Systematic workflow with visual support


Performing Automated Multi-Parametric Nanomechanical Mapping
State-of-the-art software, intuitive user guidance, and automated alignment of the detection system provide the key to autonomous operation and fast results.
The new CellHesion 300 user interface gives the operator quick and easy control of the system and its operating parameters.
The software offers an easy-to-use scripting tool for user-defined experiments. Powerful batch data processing capabilities enable the analysis and quantification of large datasets at the touch of a button.
Discover the Possibilities
Mapping of the viscoelastic properties of samples with a large topography range, over an extended frequency scale with an optional Z-scanner and NestedScanner capabilities
Studying living cells under near-physiological conditions with an extensive range of accessories for control of environmental conditions, such as temperature and CO2 levels
Automate Investigation of Large Samples
The new SmartMapping feature enables the selection of flexible, user-defined 2D shaped force maps. The optimal range of force acquisition is continuously evaluated and automatically adjusted by new large-scaled Z-motors. Using optical tiling, multiple areas of interest can be selected in advance and automatically examined, allowing the easy and effective study of large sample areas. The improved motorized stage accuracy delivers a degree of precision and velocity second to none.
Integrate Seamlessly with Optical Microscopes
CellHesion 300 can be seamlessly integrated into the latest research grade optical microscopes with advanced and super-resolution capabilities, to deliver real-time, correlative data sets for the comprehensive characterization of living biological samples. Versatile experimental setups and automated adjustment
of system parameters opens new possibilities for long-term, self-regulating experiment series. CellHesion 300 is the ideal solution for the investigation of rough surfaces, densely packed cell layers, and highly corrugated tissue samples.


Selection of Scientific Publications Using the CellHesion Technology
- Abuhattum et al., Adipose cells and tissues soften with lipid accumulation while in diabetes adipose tissue stiffens. Sci Rep 12, 10325 (2022).
- Michael et al., Measuring the elastic modulus of soft culture surfaces and three-dimensional hydrogels using atomic force microscopy. Nat Protoc 16, 2418–2449 (2021).
- Liebsch et al., Quantification of heparin’s antimetastatic effect by single-cell force spectroscopy. J Mol Recognit. 34, e2854 (2021).
- Möllmert et al., Zebrafish Spinal Cord Repair Is Accompanied by Transient Tissue Stiffening. Biophys J. 118(2), 448-463 (2020).
- Shen et al., Reduction of Liver Metastasis Stiffness Improves Response to Bevacizumab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 37(6), 800-817 (2020).
- Rheinlaender et al., Cortical cell stiffness is independent of substrate mechanics, Nat. Mater. 19, 1019–1025 (2020).
- Aaron at al., Quantification of heparin’s antimetastatic effect by single-cell force spectroscopy, J Mol Recognit., 1–11 (2020).
- Krieg et al., Atomic force microscopy- based Mechanobiology, Nature Reviews Physics 1, 41–57 (2019)
- Stylianou et al., Review Article: Atomic Force Microscopy on Biological Materials Related to Pathological Conditions, Andreas, Scanning, 8452851 (2019)
- Thompson et al., Rapid changes in tissue mechanics regulate cell behaviour in the developing embryonic brain. eLife 8:e39356 (2019)
- Miroshnikova et al., Adhesion forces and cortical tension couple cell proliferation and differentiation to drive epidermal stratification, Nat Cell Biol 20, 69–80 (2018)
- Elias et al., Tissue stiffening coordinates morphogenesis by triggering collective cell migration in vivo, Nature 554, 523-527 (2018)
- Bharadwaj et al., aV-class integrins exert dual roles on a5b1 integrins to strengthen adhesion to fibronectin, Nature Communications 8, 14348, 1-10 (2017)
- Friedrichs et al., A practical guide to quantify cell adhesion using single-cell force spectroscopy. Methods (2013)